General Nutrition Guidelines During Pregnancy
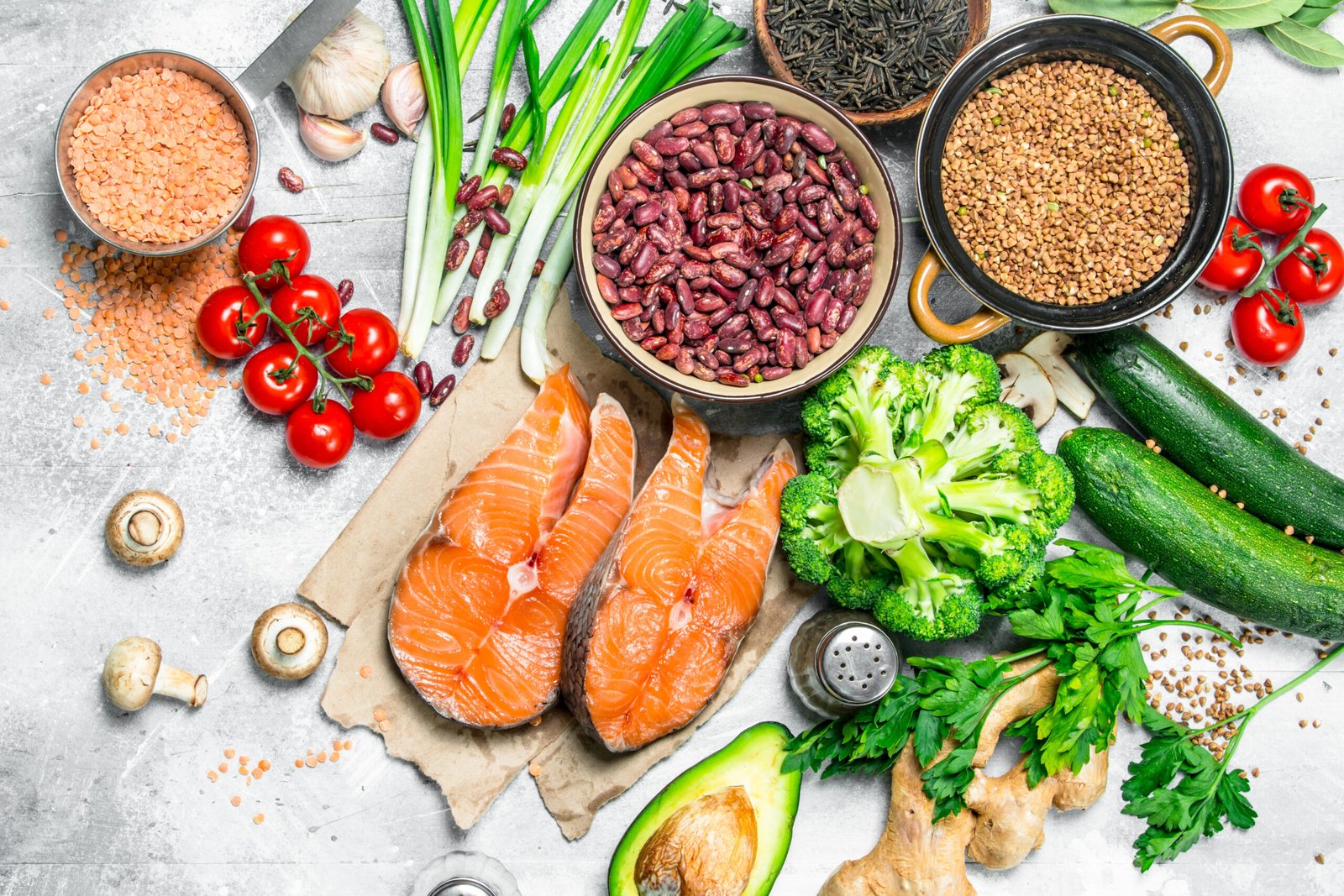
According to the Mayo Clinic and ACOG (American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists), during pregnancy, the basic principles of healthy eating remain the same:
– Get plenty of fruits and vegetables
– Choose whole grains
– Include lean protein sources
– Incorporate healthy fats
– Balance caloric intake with nutritional needs

Good nutrition during pregnancy is essential for:
– Supporting the growth of your baby
– Handling the extra demands on your body as pregnancy progresses
– Maintaining a healthy weight
– Preventing certain pregnancy complications
Caloric Needs During Pregnancy
– First trimester: No additional calories needed beyond pre-pregnancy requirements
– Second trimester: Approximately 340 extra calories per day
– Third trimester: Approximately 450 extra calories per day
These additional calories should come from nutrient-dense foods rather than empty calories.
Essential Nutrients During Pregnancy
1. Folate and Folic Acid
– Function: Helps prevent neural tube defects (serious birth defects of the brain and spine)
– Recommended amount:
– 400 micrograms (mcg) daily before pregnancy
– 600-1,000 micrograms daily during pregnancy
– Food sources:
– Fortified cereals (100-400 mcg per cup)
– Dark green leafy vegetables (spinach: 131 mcg per 1/2 cup)
– Beans (90 mcg per 1/2 cup)
– Asparagus (89 mcg per 4 spears)
– Oranges (29 mcg per small orange)
– Peanuts (27 mcg per ounce)
– Notes: Taking a prenatal vitamin with folic acid is recommended at least 3 months before conception
2. Calcium
– Function: Builds strong bones and teeth for both mother and baby; supports nerve, muscle, and blood vessel function
– Recommended amount:
– 1,000 milligrams (mg) daily for adult pregnant women
– 1,300 mg daily for pregnant teenagers
– Food sources:
– Calcium-fortified orange juice (349 mg per cup)
– Part-skim mozzarella cheese (333 mg per 1.5 oz)
– Skim milk (300 mg per cup)
– Low-fat yogurt (258 mg per 6 oz)
– Canned salmon with bones (181 mg per 3 oz)
– Spinach (123 mg per 1/2 cup)
3. Vitamin D
– Function: Works with calcium to build baby’s bones and teeth
– Recommended amount: 600 international units (IU) daily
– Food sources:
– Sockeye salmon (570 IU per 3 oz)
– Fortified milk (100 IU per cup)
– Fortified orange juice (100 IU per 8 oz)
– Eggs (43.5 IU per large egg)
– Notes: Most pregnant women need vitamin D supplements as it can be difficult to get enough from diet alone
4. Protein
– Function: Crucial for fetal growth and development
– Recommended amount: 71 grams (g) daily
– Food sources:
– Low-fat cottage cheese (28 g per cup)
– Chicken breast (26 g per 3 oz)
– Canned salmon (17 g per 3 oz)
– Lentils (9 g per 1/2 cup)
– Skim milk (8 g per cup)
– Peanut butter (7 g per 2 tablespoons)
– Eggs (6 g per large egg)
-Protein powders – vegetarian or animal derived can add to shake, coffee
5. Iron
– Function: Helps prevent iron deficiency anemia; supports increased blood volume and oxygen delivery to the fetus
– Recommended amount: 27 milligrams (mg) daily
– Food sources:
– Iron-fortified cereals (20 mg per 1/2 cup)
– Lean beef (3 mg per 3 oz)
– Spinach (3 mg per 1/2 cup)
– Kidney beans (2 mg per 1/2 cup)
– Dark turkey meat (1 mg per 3 oz)
– Notes:
– Iron from animal sources is more easily absorbed
– Pair plant-based iron sources with vitamin C-rich foods to enhance absorption
– Many healthcare providers recommend iron supplements during pregnancy
6. Choline
– Function: Supports fetal brain development and helps prevent neural tube defects
– Recommended amount: 450 mg daily
– Food sources:
– Eggs (147 mg per large egg)
– Beef liver (356 mg per 3 oz)
– Chicken breast (72 mg per 3 oz)
– Soybeans (107 mg per 1/2 cup)
7. Omega-3 Fatty Acids (DHA)
– Function: Supports fetal brain and eye development
– Recommended amount: At least 200-300 mg DHA daily
– Food sources:
– Fatty fish like salmon (1,240 mg per 3 oz)
– Fortified eggs
– Walnuts
– Flaxseed
– Notes: For women who don’t eat fish, a DHA supplement may be recommended
Enough Omega-3 “good fats’ very important for brain development
Prenatal Vitamins
– Recommended for all pregnant women, ideally starting at least 3 months before conception
– Should contain:
– Folic acid (400-800 mcg)
– Iron (27 mg)
– Calcium (250 mg or more)
– Vitamin D (400 IU or more)
– DHA (200 mg or more)
– Best taken with food to minimize nausea
– Should be continued throughout pregnancy and while breastfeeding
Foods to Limit or Avoid During Pregnancy
– High-mercury fish (shark, swordfish, king mackerel, tilefish)
– Raw or undercooked meat, poultry, eggs, and seafood
– Unpasteurized dairy products and juices
– Excessive caffeine (limit to 200 mg daily, about one 12-oz cup of coffee)
– Alcohol (no safe amount during pregnancy)
– Unwashed fruits and vegetables
– Certain herbal teas and supplements (consult healthcare provider)
Sources
– American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), 2023
– Mayo Clinic, “Pregnancy diet: Focus on these essential nutrients,” 2025
– U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025